Mononucleosis, commonly known as mono, is a viral infection most often caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). After exposure to the virus, symptoms don't appear immediately. Instead, there's an incubation period during which the virus silently multiplies in the body. Typically, symptoms begin to surface four to six weeks after initial exposure, though this timeframe can vary depending on the individual's immune response and overall health. Understanding this delay is crucial for ...
Why You Need to Wear SPF Even When It's Cold Outside
Even during the early spring months when the temperature is cool and the sun seems less intense, wearing sunscreen is crucial for protecting your skin. Ultraviolet (UV) rays, which cause skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer, are present year-round, even on cloudy or cold days. Up to 80% of UV rays can reach your skin on overcast days, and snow or reflective surfaces can amplify exposure. So, regardless of the weather, applying ...
How to Treat a Dry Cough
Coughing is a reflex to clear the airways of debris and irritation. Many different illnesses and irritants can lead to a cough, which can make it difficult to diagnose and treat the underlying cause of your symptoms. If you’re experiencing a dry cough, it is important to seek medical treatment for proper diagnosis and treatment. At AFC Urgent Care Grand Junction, our walk-in clinic offers same-day care for coughs 7 days a week. If ...
Dispelling Myths: Can Adults Get Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
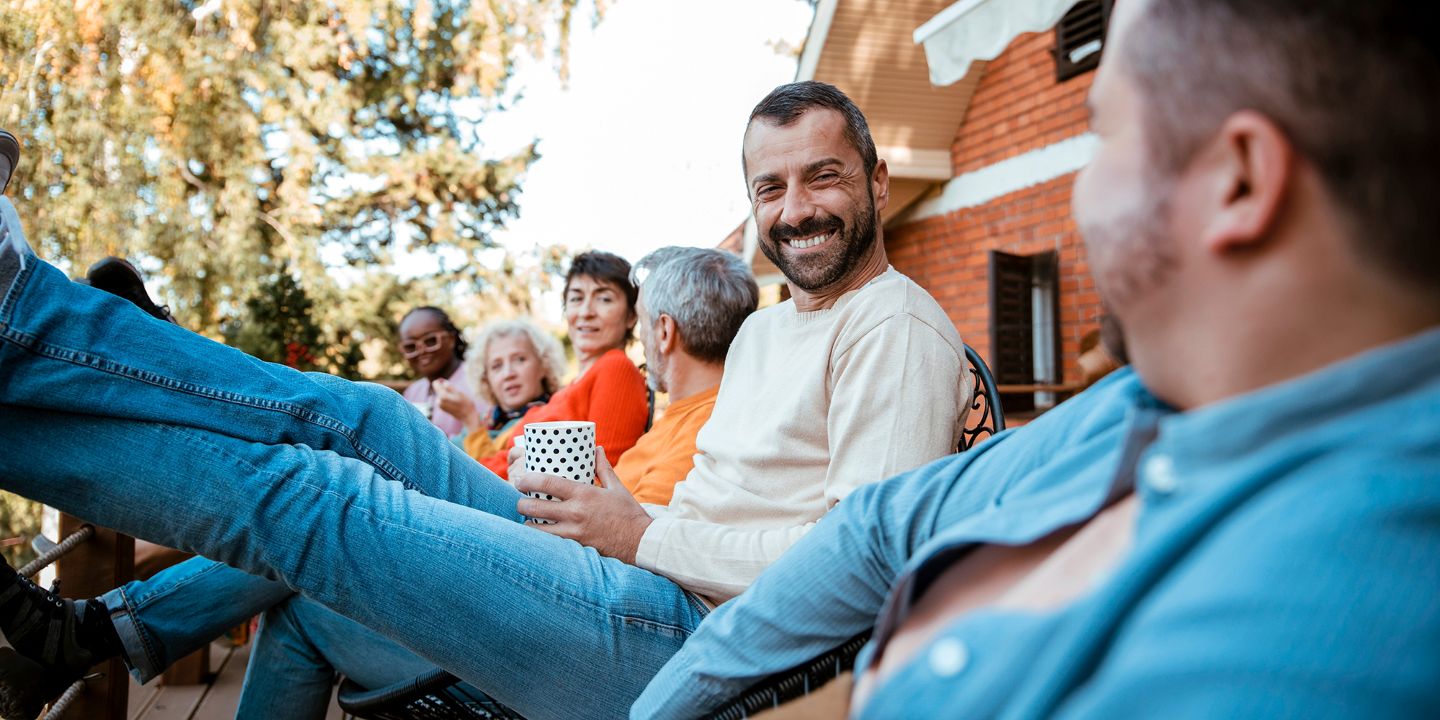

HFMD is often perceived as an illness that only impacts young children, but adults can get hand, foot, and mouth, too. Dispelling the myth that HFMD exclusively affects children is critical, especially since adults may not realize they're carrying the virus and could inadvertently spread it. Pre-Register What Is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease? HFMD is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects young children, typically those under the age of five. It ...
Can the Flu Cause Vomiting?
Feeling sick is an all too common occurrence in the winter months. When temperatures drop, cold weather can cause our immune system to weaken and we tend to spend more time indoors close to others. These factors facilitate the rapid spread of disease, including viral infections like the flu. The flu can cause many different symptoms, however, it typically impacts the upper respiratory system including your lungs and throat. It is unlikely for the flu ...
How Long Do Fevers Last in Infants?
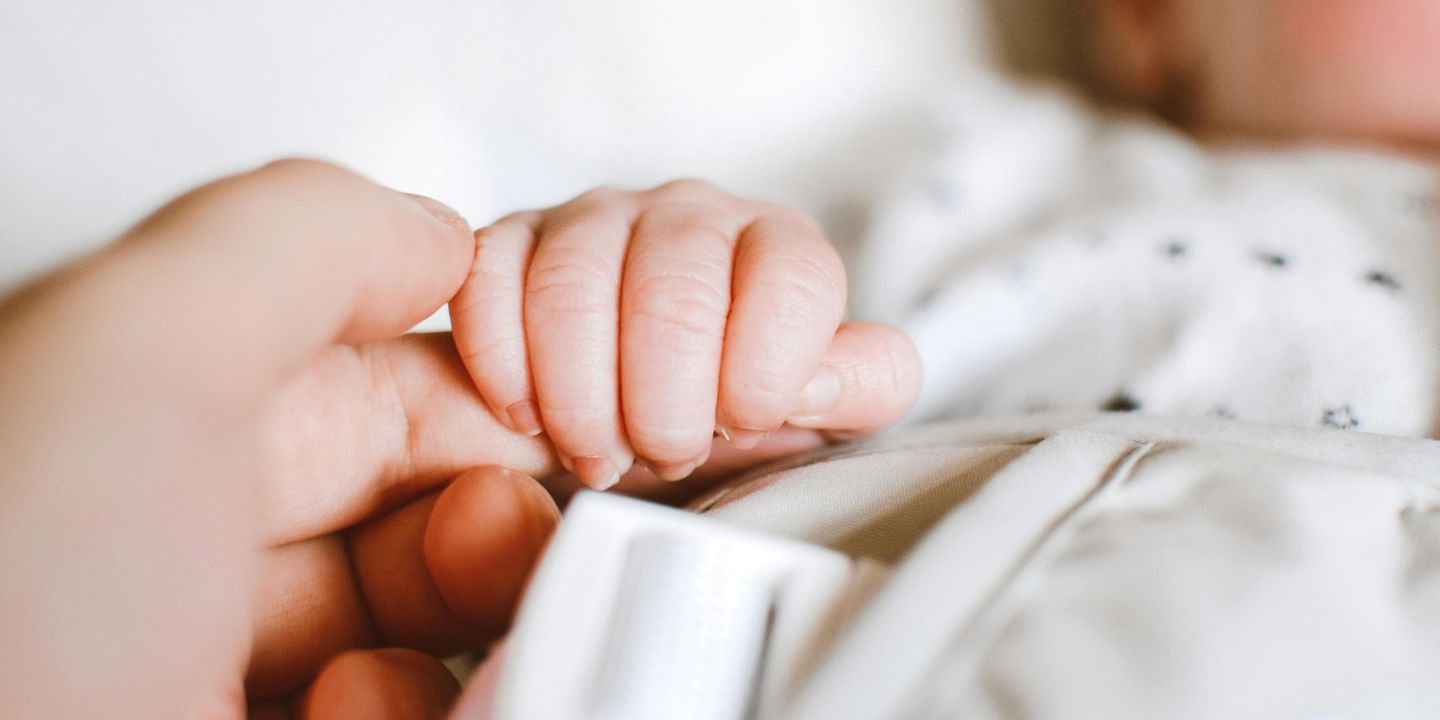

When your little one develops a fever, it's natural to worry and wonder, "How long do fevers last in infants?" Fevers are often the body's way of fighting infections by creating a less hospitable environment for germs. While fevers can seem concerning, they are usually not harmful and often resolve on their own. Pre-Register Understanding How Long Fevers Last in Infants In most cases, fevers in infants last around two to three days ...
Are Sugar Rushes Real and How Do They Work?
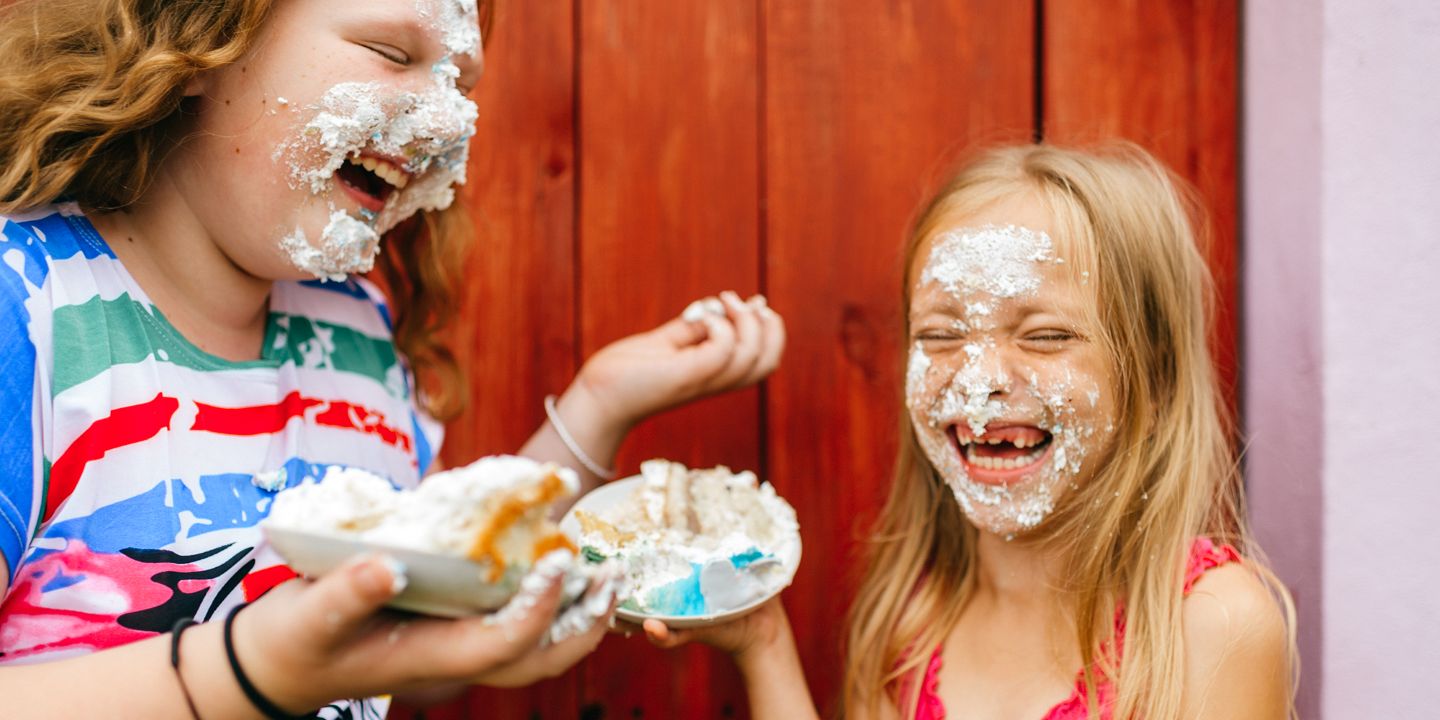

Are sugar rushes real? For decades, many parents have believed in the idea of a “sugar rush,” a phenomenon where kids become hyperactive after consuming sugary snacks or drinks. This belief has led to widespread efforts to limit sugar intake, especially during times when parents want their children to stay calm and focused. Despite its popularity, scientific research shows that the so-called sugar rush is actually a myth. In this blog post, we'll explore ...
Does Menopause Make You Tired? A Guide to Symptoms and Support
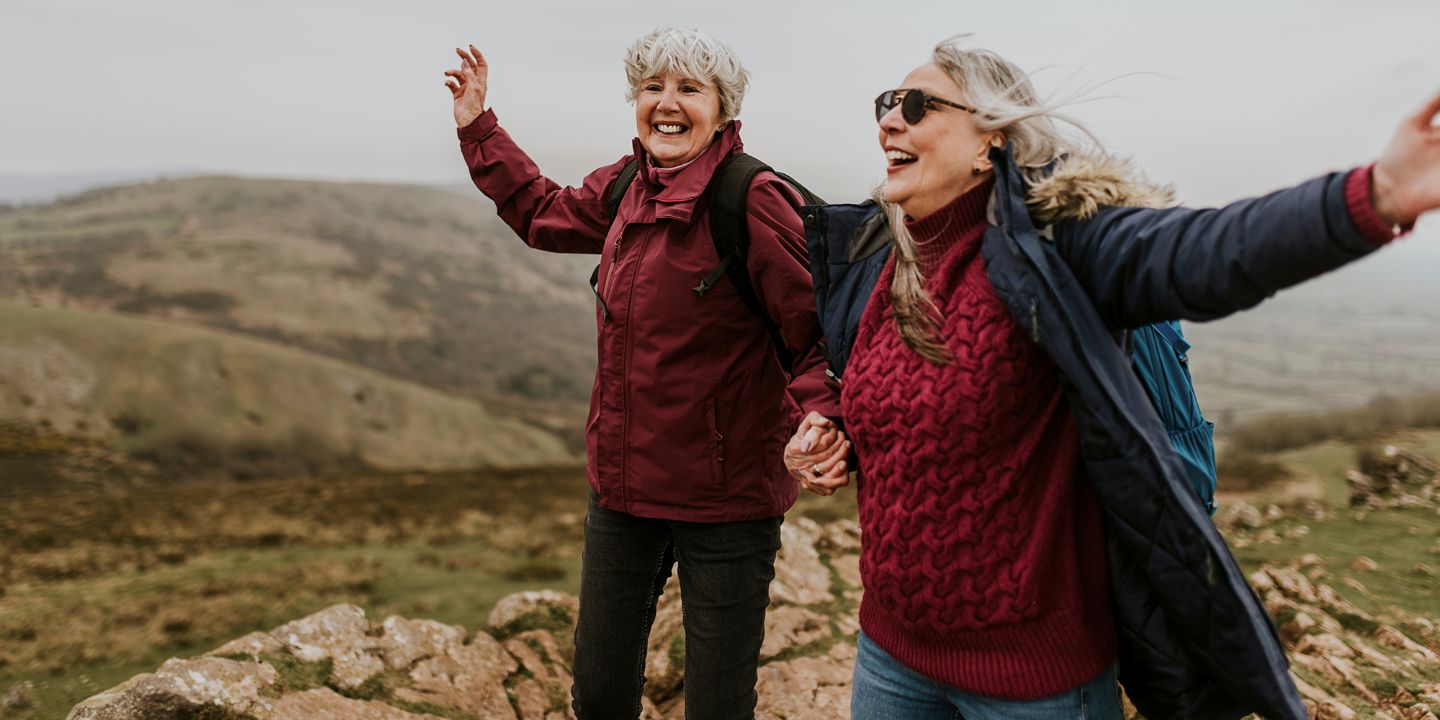

Does menopause make you tired? Menopause is a natural phase in a woman’s life, marking the end of her reproductive years. While it’s often associated with hot flashes and mood swings, many women also experience persistent fatigue during this transition. Feeling tired or low on energy can be frustrating and disruptive, especially when combined with other menopause symptoms. Pre-Register Understanding Menopause Menopause is a natural biological process that occurs when a woman’s ...
What Is the Best Diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome?

You may wonder, "What is the best diet for irritable bowel syndrome?" The answer depends on your unique symptoms and needs, but several dietary strategies have been known to bring relief. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common condition that affects millions of people, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. While there isn’t a one-size-fits-all cure for IBS, making thoughtful changes to your diet can play a significant role in ...
Wrist Sprain: How to Heal Quickly

A wrist sprain is painful and can worsen without proper care. Explore options for treatment and when to seek medical attention. Pre-Register Table of Contents How To Tell if You Have a Sprained Wrist Severity of Sprained Wrists How To Treat a Sprained Wrist How To Heal a Sprained Wrist Fast Sprained Wrist Medical Devices Should I Go to the ER or Urgent Care? Activities to Avoid With a Sprained Wrist Visit AFC for Help ...
How To Treat A Productive Cough
Coughing is a common symptom of many different illnesses. Determining the cause of your cough is the best way to treat it. However, a productive cough can be caused by many different types of infections. If you’re coughing up mucus, you may be suffering from a respiratory tract infection. Keep reading to learn how to treat a productive cough and common causes of a cough that produces mucus. For same-day illness symptom treatment, walk ...
Is It Normal for Cold Symptoms to Last 2 Weeks?
It is frustrating and sometimes alarming when a cold appears to drag on longer than you expect it to. Although most colds clear up before 10 days, some colds can have symptoms that extend more than two weeks. Knowing why this happens, when it is considered a normal course of recovery, and when it may be something serious are all important pieces of information to help you determine the best course of action to treat ...
Deep Cut Treatment: What to Do & When to Get Stitches

If you get a deep cut, you may be able to treat it without stitches. Learn more about treating a deep cut. Pre-Register Table of Contents What is Considered a Deep Cut? How Deep Does a Cut Need to Be for Stitches? Treatment Other Concerns to Keep in Mind Where To Go for Treatment What is Considered a Deep Cut? A deep laceration is generally considered over a quarter inch deep, but this also depends ...
Stomach Pain After Eating: What's Causing It & How To Fix It

Stomach pain after eating can be a cause for concern, especially if it happens frequently. Learn more about treating frequent and occasional stomach pain. Pre-Register Table of Contents Potential Causes and Treatments Upper Stomach vs. Lower Stomach Pain What To Do If Other Symptoms, like Diarrhea, Accompany the Stomach Pain What Do I Do If My Stomach Pain After Eating is Frequent? When Do I Need to See a Medical Provider? Potential Causes and Treatments ...
Ear Bleeding: Causes, Treatment & When to Seek Medical Attention
Ear bleeding can be a sign of serious medical problems, especially if you’ve fallen or had head trauma. Explore potential ear bleeding causes and treatments. Pre-Register Table of Contents Middle or Outer Ear Infection Head Trauma or Falling Torn or Ruptured Eardrum Foreign Object Barotrauma Other Infections Other Symptoms To Watch For When To Visit a Healthcare Provider Visit Your Local AFC Middle or Outer Ear Infection Infections in the ear, whether in the ...
Lingering Cough After Cold: How to Get Rid of Your Residual Symptoms

A lingering cough after a cold can be irritating and exhausting. Use these tips to get rid of your residual cough. Table of Contents What Causes a Lingering Cough How to Get Rid of a Chronic Cough Medications to Try When to See a Provider Visit Your Local AFC What Causes a Lingering Cough One of the most common causes of a chronic cough is a postnasal drip caused by allergies or a cold. Plus ...
Signs You May Have Bronchitis
Winter is peak respiratory illness season. While colds and the flu tend to spread like wildfire at this time, other illnesses also can spread quickly and cause unpleasant symptoms. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from your lungs. It can be either acute or chronic, with symptoms often overlapping between the two. If you are experiencing persistent coughing, wheezing, or mucus production, you might have bronchitis. Other common ...
Why Is My Cold Getting Worse
When you catch a cold, it's common to experience mild symptoms like a sore throat, congestion, and fatigue. However, sometimes those symptoms worsen instead of improve over time. There are several reasons why a cold may worsen over time instead of improve. Potential reasons why your symptoms may be worsening include complications like secondary infections, not getting enough rest, or even misdiagnosis of your symptoms. If you’re experiencing illness symptoms that just won ...
The Relationship Between Technology and Sleep

Technology has become an integral part of our daily lives, including our bedtime routines. Many people use electronic devices right before bed, whether scrolling through social media, watching TV, or responding to emails, leading to much research into the relationship between technology and sleep. Join us as we explore how technology affects sleep, debunk common myths, and offer practical tips for creating a more restful, tech-free sleep environment. Table of Contents How Technology and Sleep ...
How Long Does Vertigo Last?

Vertigo is common yet unsettling - for some, vertigo is a mild inconvenience, while it can significantly disrupt daily life for others. But how long does vertigo last? Whether you're experiencing brief episodes or ongoing bouts, the duration of vertigo largely depends on the underlying cause and the type of vertigo you have. Table of Contents What Is Vertigo? How Long Does Vertigo Last? Can Stress Cause Vertigo? How to Prevent Vertigo Visit AFC ${city ...
Archives
- April 2025 (2)
- March 2025 (1)
- February 2025 (7)
- January 2025 (6)
- December 2024 (8)
- November 2024 (4)
- October 2024 (3)
- September 2024 (6)
- August 2024 (6)
- July 2024 (8)
- June 2024 (4)
- May 2024 (6)
- April 2024 (4)
- March 2024 (7)
- February 2024 (2)
- January 2024 (2)
- December 2023 (14)
- November 2023 (4)
- October 2023 (3)
- September 2023 (3)
- August 2023 (3)
- July 2023 (1)
- June 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (1)
- April 2023 (3)
- March 2023 (1)
- February 2023 (3)
